GitHub has put out an advisory detailing what may be an ongoing phishing campaign targeting its users to steal credentials and two-factor authentication (2FA) codes by impersonating the CircleCI DevOps platform.
The Microsoft-owned code hosting service said it learned of the attack on September 16, 2022, adding the campaign impacted "many victim organizations."
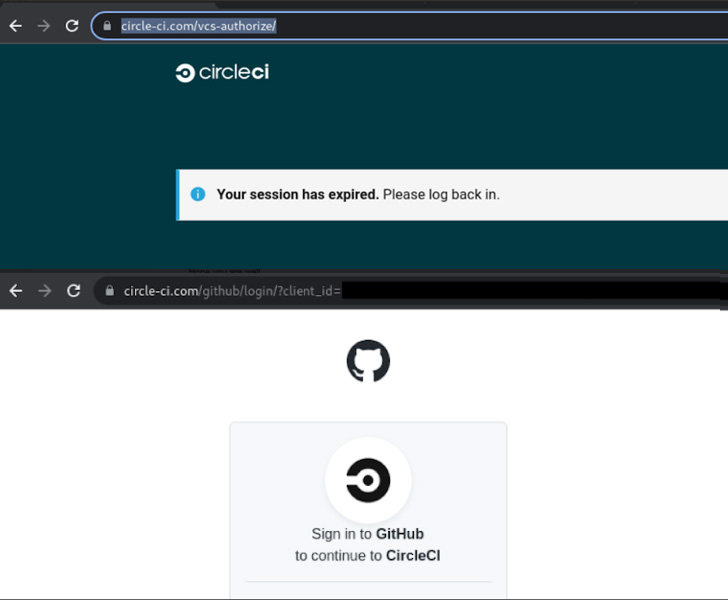
The fraudulent messages claim to notify users that their CircleCI sessions have expired and that they should log in using GitHub credentials by clicking on a link.
Another bogus email revealed by CircleCI prompts users to sign in to their GitHub accounts to accept the company's new Terms of Use and Privacy Policy by following the link embedded in the message.
Regardless of the lure, doing so redirects the target to a lookalike GitHub login page designed to steal and exfiltrate the entered credentials as well as the Time-based One Time Password (TOTP) codes in real-time to the attacker, effectively allowing a 2FA bypass.
"Accounts protected by hardware security keys are not vulnerable to this attack," GitHub's Alexis Wales said.
Among other tactics embraced by the threat actor upon gaining unauthorized access to the user account include creating GitHub personal access tokens (PATs), authorizing OAuth applications, or adding SSH keys to maintain access even after a password change.
The attacker has also been spotted downloading private repository contents, and even creating and adding new GitHub accounts to an organization should the compromised account have organization management permissions.
GitHub said it has taken steps to reset passwords and remove maliciously-added credentials for impacted users, alongside notifying those affected and suspending the actor-controlled accounts. It did not disclose the scale of the attack.
The company is further urging organizations to consider using phishing-resistant hardware security keys to prevent such attacks.
The latest phishing attack comes a little over five months after GitHub suffered a highly targeted campaign that resulted in the abuse of third-party OAuth user tokens maintained by Heroku and Travis CI to download private repositories.







0 Comments